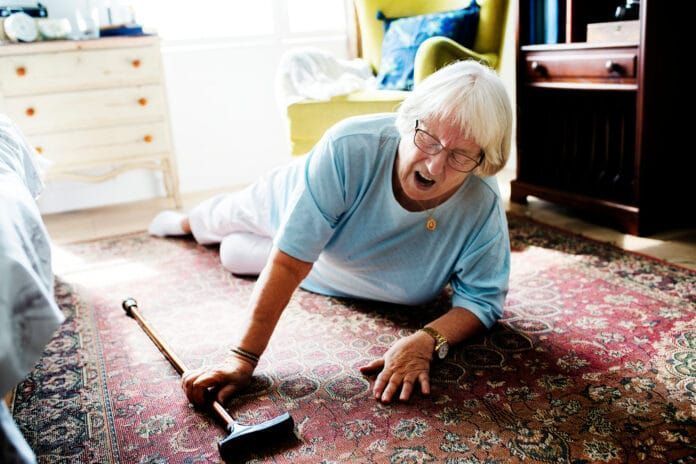

5 risk factors for osteoporosis’a fracture of the neck of the femur
An unfortunate fall in the elderly can lead to serious consequences, including a fracture of the neck of the femur. What are the risk factors of a femoral neck fracture? ? How to avoid fracturing your femoral neck ?
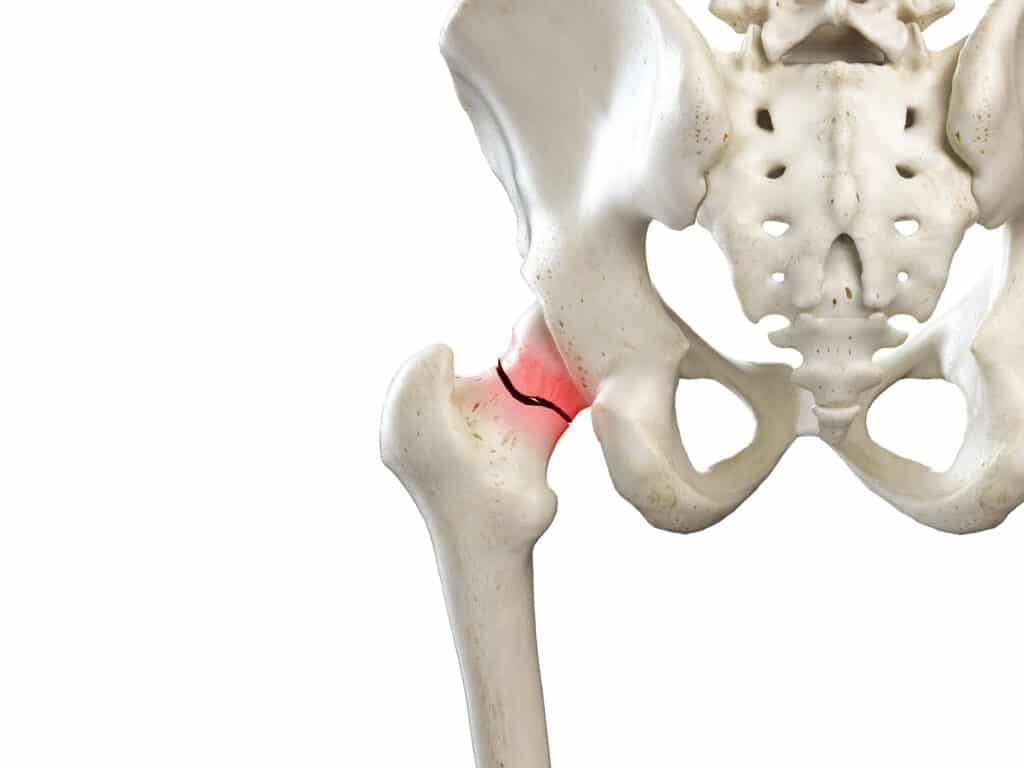
A fracture of the neck of the femur: what is it ?
Located at the top of the femur, the neck of the femur is the upper end of the bone that fits into the pelvis. It is therefore important to prevent a fracture of the femur in order to’avoid severe pain.
A femoral neck fracture or hip fracture is a crack that weakens the femoral head. There are three types of fractures: intertrochanteric, subcapital or cervical depending on the area affected on the femoral neck.
The fracture of the neck of the femur is the most common fracture in the elderly and more particularly in women, more prone to osteoporosis.
Although most of the time it is not serious, it leads to severe pain and a loss of autonomy.
In the most severe cases, a fracture of the neck of the femur This can have more disabling consequences such as knee stiffness, osteoarthritis, but also fat embolism syndrome (FES). When a fracture occurs, fatty pellets can clog the pulmonary and systemic vessels and cause respiratory, skin, neurological and hematological symptoms.
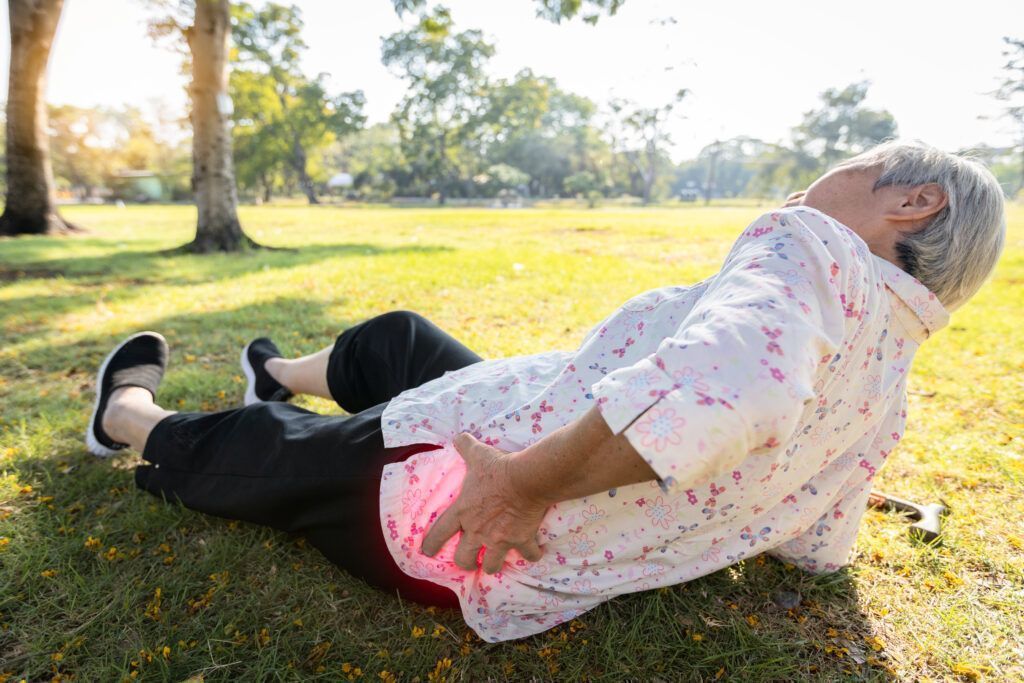
5 risk factors for a femoral neck fracture
The best way to prevent a femur fracture is to know all the risk factors. Here they are !
The older you get, the more your bone density and muscle mass decrease. After the age of 80, the bones become more fragile and the slightest fall or trauma can lead to bone fractures. Poor vision and balance also increase the risk of falling.
Sex
Women are more severely affected than men (3 women to 1 man). After menopause, estrogen levels drop sharply, which accelerates the onset of osteoporosis, especially in the case of early menopause.
Heredity
Some people are more likely to suffer from osteoporosis and therefore have a higher risk of a femoral neck fracture. People who are short or have small bones, Caucasians and Asians are often more prone to femoral fractures.
Lifestyle
- Poor nutrition has an impact on bone health as we age. People who have had a calcium or vitamin D deficiency see their bone mass decrease as they age.
- Anorexia or bulimia also impact the construction of the skeleton by depriving the body of essential nutrients.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption deteriorate bones.
- Lack of physical activity also plays a role, as sports activities such as walking strengthen the bone structure and muscles.
Drugs and certain pathologies
Unfortunately, certain medications taken in prolonged treatment such as corticosteroids weaken bones and muscles.

Several diseases and health conditions are known to weaken bones and increase the risk of fracture:
- Type 1 diabetes.
- Gastrointestinal disorders.
- Rheumatoid problems.
- Diseases of the nervous system such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis.
- Inflammatory diseases.
- Kidney failure.
- Dementia.
If you cannot prevent certain risk factors (aging and heredity), you can act as soon as possible on the other factors by adopting a healthy lifestyle:
- Practicing sports on a regular basis.
- Changing your eating habits to a healthier and more balanced diet.
- Increase your vitamin and calcium intake.
- Limit non-essential drug treatments.
Note that all these tips are the same to prevent osteoporosis !
To avoid surgery on the neck of the femur, think about adapting your home to to keep you from falling over ! Treatments for femoral neck fractures (hip replacements, metal plates, screws to stabilize the fracture) are effective, but prevention is even more so. Especially since 20% of cervical fracture victims die as a result of the accident and 50% have permanent after-effects..